Template-Based Static Binding
Unreal has a lot of C++ functions and classes without reflection tags. In order to access them within TypeScript, Template-based static binding should be used.
Table Of Contents
Setup
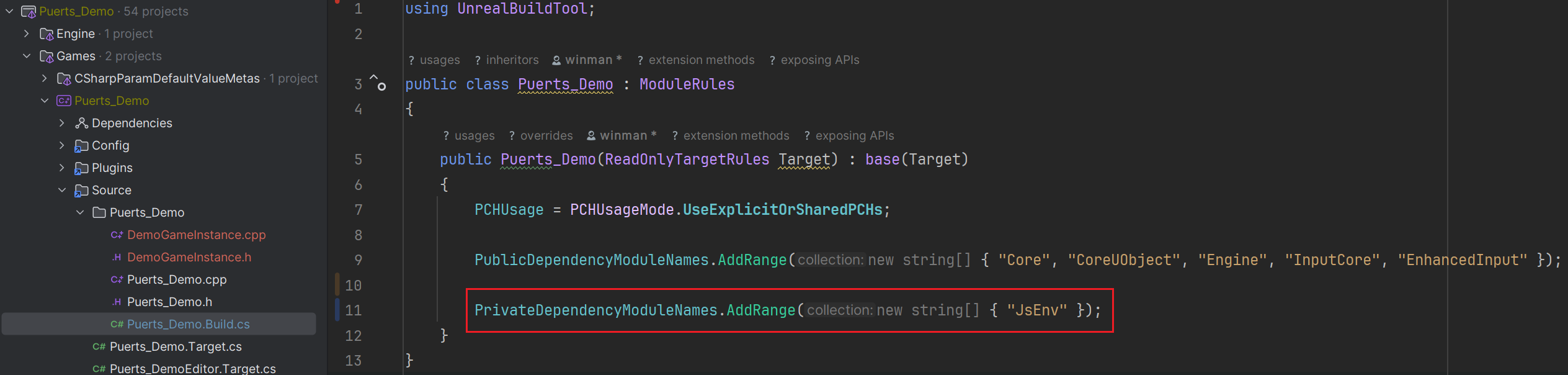
In order for C++ to register puerts modules, dependencies must be added to the *.Build.cs file.
For template based static binding, JsEnv is required.
Usage
Unreal Engine Class
C++
// UObject_Bindings.h
#pragma once
#include "Binding.hpp"
#include "UEDataBinding.hpp"
// Define all used types
UsingUClass(UObject)
UsingUClass(UWorld)
UsingUClass(UClass)
class UObject_Bindings
{
public:
UObject_Bindings()
{
puerts::DefineClass<UObject>()
.Method("GetWorld", MakeFunction(&UObject::GetWorld))
.Method("GetClass", MakeFunction(&UObject::GetClass))
.Method("IsValid", MakeFunction(&UObject::IsValidLowLevel))
.Register();
}
};
inline UObject_Bindings UObject_Bindings_Registrar;
TypeScript
if (MyUObj?.IsValid())
{
const World = MyUObj?.GetWorld();
const ObjectClass = MyUObj?.GetClass();
}
Regular C++ Class
C++
// ExampleClass.h
#pragma once
class ExampleClass
{
// Static
public:
static int StaticAdd(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
inline static int StaticInt{30035};
// Non-Static
public:
int GetRegularInt()
{
return RegularInt;
}
int RegularInt{1337};
};
// ExampleClass_Bindings.h
#pragma once
#include "Binding.hpp"
#include "ExampleClass.h"
// Define all used types
UsingCppType(ExampleClass);
class ExampleClass_Bindings
{
public:
ExampleClass_Bindings()
{
puerts::DefineClass<ExampleClass>()
.Function("StaticAdd", MakeFunction(&ExampleClass::StaticAdd)) // Static Function
.Variable("StaticInt", MakeVariable(&ExampleClass::StaticInt)) // Static Variable
.Method("GetRegularInt", MakeFunction(&ExampleClass::GetRegularInt)) // Member Function
.Property("RegularInt", MakeProperty(&ExampleClass::RegularInt)) // Member Variable
.Register();
}
};
inline ExampleClass_Bindings ExampleClass_Bindings_Registrar;
TypeScript
import * as Cpp from 'cpp'
console.log("Static Int = " + Cpp.ExampleClass.StaticInt);
const AddedResult = Cpp.ExampleClass.StaticAdd(12, 34);
console.log("StaticAdd(12, 34) = " + AddedResult);
const ExampleClass = new Cpp.ExampleClass();
console.log("GetRegularInt() = " + ExampleClass?.GetRegularInt());
console.log("RegularInt = " + ExampleClass?.RegularInt);
Note: After defining a classes bindings, compile the C++, restart Unreal Engine and regenerate TypeScript definitions
API Reference
Function Decaleration
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
.Method(Name, Function Reference) | Exposes a member function to TypeScript |
.Function(Name, Function Reference) | Exposes a static function to TypeScript |
Function Referencing
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
MakeFunction(Reference To Function) | Creates a member function reference |
MakeCheckFunction(Reference To Function) | Creates a member function reference with parameter varification |
SelectFunction(ReturnType... (ClassName::*)(Parameters...), Reference To Function) | Creates a member function reference based on a single function overload |
If the function has multiple overloads:
C++
CombineOverloads(
MakeOverload(void (ExampleClass::*)(), &ExampleClass::ExampleFunction),
// More Overloads...
)
Variable Deceleration
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
.Property(Name, Variable Reference) | Exposes a member variable to TypeScript |
.Variable(Name, Variable Reference) | Exposes a static variable to TypeScript |
Variable Referencing
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
MakeProperty(Reference To Variable) | Creates a member variable reference |
MakePropertyByGetterSetter(&ClassName::GetterFunction, &ClassName::SetterFunction) | Creates a member variable reference proxied through getter and setter functions |
MakeVariable(Reference To Variable) | Creates a static variable reference |
Constructor Deceleration
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
.Constructor() | Exposes the default constructor to TypeScript |
.Constructor<Arg1Type, Arg2Type, ...>() | Exposes a specified constructor with arguments to TypeScript |
If the constructor has multiple overloads:
C++
.Constructor(
CombineConstructors(
MakeConstructor(ExampleClass),
MakeConstructor(ExampleClass, int),
// More overloads...
))
Inheritance
C++
// ExampleBaseClass.h
#pragma once
class ExampleBaseClass
{
public:
virtual int VirtualMemberFunction()
{
return -1;
}
};
// ExampleBaseClass_Bindings.h
#pragma once
#include "Binding.hpp"
#include "ExampleBaseClass.h"
UsingCppType(ExampleBaseClass);
class ExampleBaseClass_Bindings
{
public:
ExampleBaseClass_Bindings()
{
puerts::DefineClass<ExampleBaseClass>()
.Method("VirtualMemberFunction", MakeFunction(&ExampleBaseClass::VirtualMemberFunction))
.Register();
}
};
inline ExampleBaseClass_Bindings ExampleBaseClass_Bindings_Registrar;
// ExampleChildClass.h
#pragma once
#include "ExampleBaseClass.h"
class ExampleChildClass : public ExampleBaseClass
{
public:
virtual int VirtualMemberFunction() override
{
// Overrided Implementation
return 1337;
}
};
// ExampleChildClass_Bindings.h
#pragma once
#include "Binding.hpp"
#include "ExampleChildClass.h"
UsingCppType(ExampleChildClass);
class ExampleChildClass_Bindings
{
public:
ExampleChildClass_Bindings()
{
puerts::DefineClass<ExampleChildClass>()
.Extends<ExampleBaseClass>()
.Register();
}
};
inline ExampleChildClass_Bindings ExampleChildClass_Bindings_Registrar;